3 Manipulating Columns
| Select columns | select(), pull() |
| Arrange columns | relocate(), select() |
| Add columns | mutate(), transmute(), bind_cols() |
| Rename columns | rename() |
Please copy the following code and paste them into a script in the RStudio. We will walk through them with the visual explanations from the dplyr cheat sheet.
Input
# Sample code from the dplyr cheat sheet
## 3.1 Select columns
pullmt=pull(mtcars, wt)
selectmt=select(mtcars, mpg, wt)
## 3.2 Arrange columns
relocatemt=relocate(mtcars, mpg, cyl, .after = last_col())
## 3.3 Add columns
mutmt=mutate(mtcars, gpm = 1 / mpg)
tmt=transmute(mtcars, gpm = 1 / mpg)
### A showcase for bind_cols
x <- data.frame(
A = c('a', 'b', 'c'),
B = c('t', 'u', 'v'),
C = c(1, 2, 3))
x
y <- data.frame(
E = c('a', 'b', 'd'),
G = c('t', 'u', 'w'), #skip F because F = FALSE, so it's best not to use that letter.
H = c(3, 2, 1))
y
# You have to make sure the binding is meaningful by yourself.
# This is not the same as joins
bind_cols(x, y)
## 3.4 Rename columns
rename(cars, distance = dist)
Visual walkthrough
Select columns: select() and pull()

What to notice: these functions keep only the columns you ask for, which narrows your data to relevant variables.
Arrange columns: relocate()

What to notice: this changes column order only; rows and values stay the same.
Add columns: mutate() and transmute()
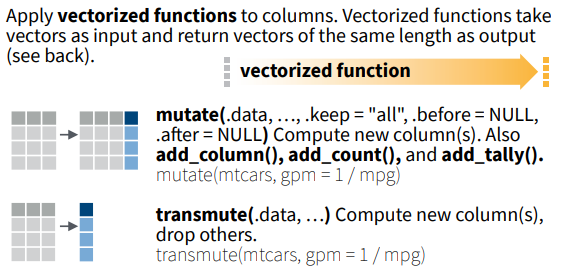
What to notice: mutate() adds new columns while keeping existing ones, but transmute() keeps only new columns.
Rename columns: rename()

What to notice: only the column names change; the data inside each column does not.
Combine columns from multiple data frames: bind_cols()
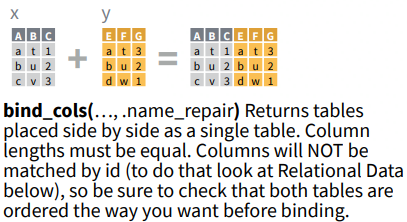
What to notice: bind_cols() joins data by row position, so use it only when rows correspond correctly.
Practice 2
iris is a data frame with 150 cases (rows) and 5 variables (columns) named Sepal.Length, Sepal.Width, Petal.Length, Petal.Width, and Species. Make a new data frame which contains only Species and the ratio of Petal.Width and Petal.Length.
click here for solution
iris$Species=str_replace(iris$Species,
"setosa",
"bristle-pointed iris")
This page is meant to introduce functions that help manipulate columns.
Loading last updated date...