Classification & Clustering
Classification and clustering are two important types of machine learning techniques. Classification uses supervised learning, where the algorithm is trained on a labeled dataset to learn the relationship between input features and output class labels. The trained model can then be used to predict the class labels of new, unseen data. Clustering uses unsupervised learning, where the algorithm groups similar data points together based on their similarity or distance from each other. The number of clusters may be predefined or learned from the data.
Classification outputs a discrete class label for each input, based on the learned mapping function. The output is interpretable and can be used for decision-making. Clustering outputs a set of clusters or groups, which may or may not have an interpretable label. The output can be used for exploratory data analysis or as a preprocessing step for other tasks.
Classification models can be evaluated using metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score, which measure the performance of the model in predicting the correct class labels. Clustering models can be evaluated using metrics such as silhouette coefficient, Calinski-Harabasz index, and Davies-Bouldin index, which measure the quality of the clusters based on their compactness, separation, and similarity.
Classification Metrics:
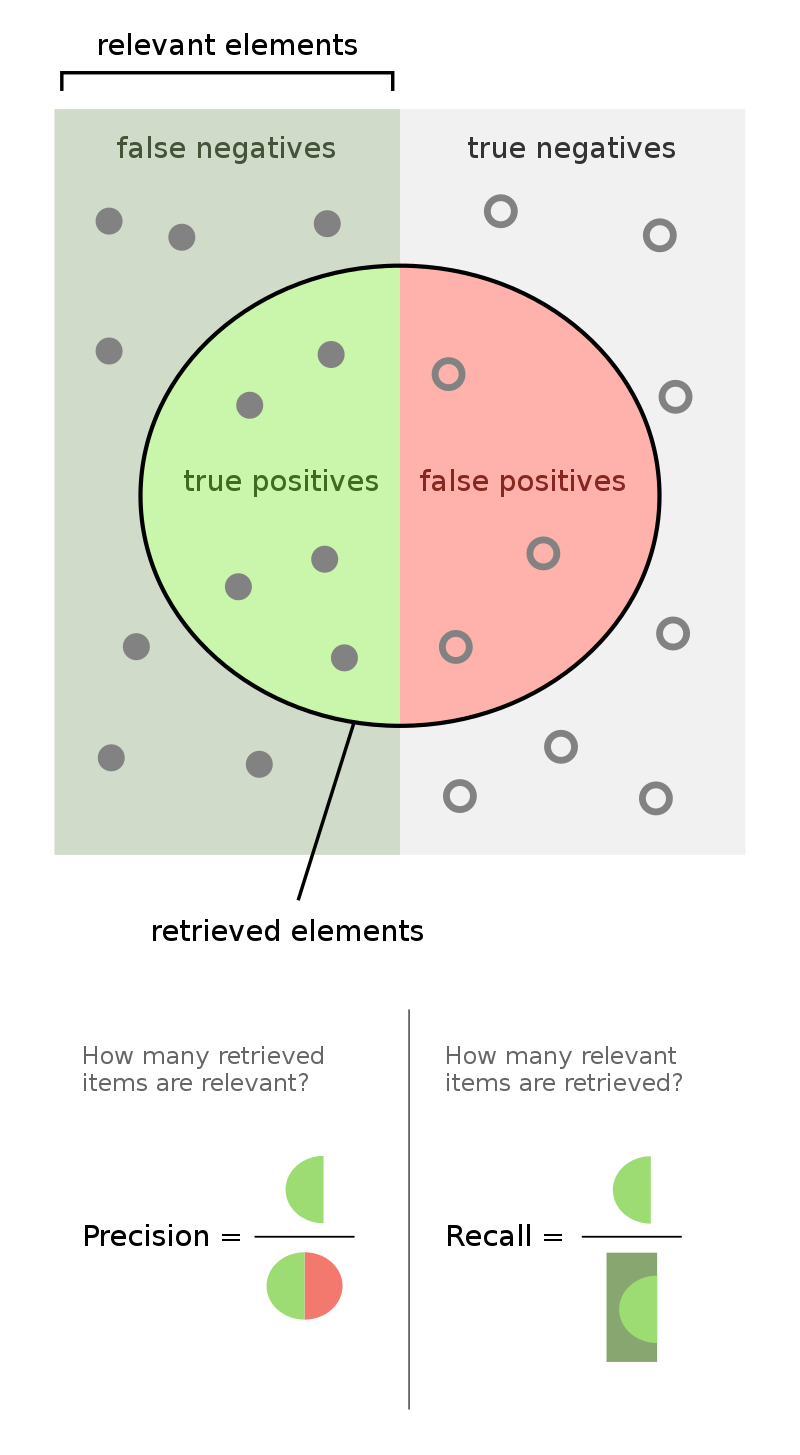
Accuracy: The proportion of correctly classified instances to the total number of instances.
Precision: The proportion of true positive instances to the total number of instances that are classified as positive.
Recall: The proportion of true positive instances to the total number of instances that belong to the positive class.
There are several types of classification and clustering algorithms, each with their own strengths and limitations. Here are some of the most commonly used types of classification and clustering:
Classification Algorithms
Logistic Regression: Logistic Regression is a simple and widely used binary classification algorithm that uses a logistic function to map input features to a binary outcome, making it suitable for binary classification tasks.
Decision Trees: Decision Trees are tree-like structures where each internal node represents a feature, and each leaf node represents a class label. Decision Trees recursively split the data based on the values of input features to make decisions about the class labels. They are easy to interpret and can handle both binary and multi-class classification tasks. Random Forest is an ensemble technique that combines multiple decision trees to improve the accuracy and robustness of classification. Random Forests can handle high-dimensional data and are less prone to overfitting compared to individual decision trees.
Support Vector Machines (SVM): SVM is a powerful binary classification algorithm that finds the optimal hyperplane that separates the data into different classes with the maximum margin. SVM can handle both linear and nonlinear classification tasks using different kernel functions.
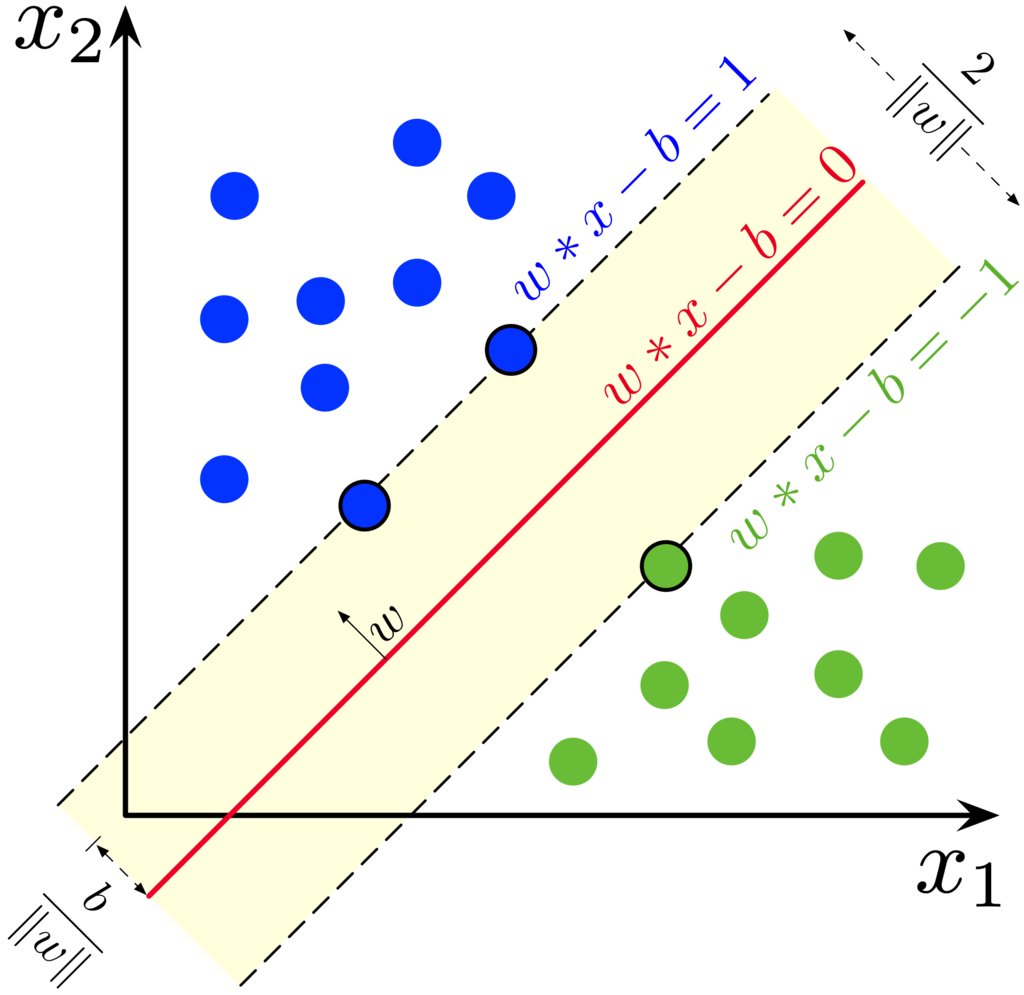
From Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Support_vector_machine
Clustering Algorithms
K-Means Clustering: K-means clustering is the most widely used type of clustering algorithm. It involves dividing a dataset into k clusters, where k is a user-defined parameter. The algorithm iteratively assigns data points to the nearest cluster center and recalculates the cluster center until convergence.
Hierarchical Clustering: Hierarchical clustering is a type of clustering algorithm that creates a tree-like structure of clusters, called a dendrogram. It can be divided into two types: agglomerative, which starts with each data point as its own cluster and iteratively merges the closest pairs of clusters, and divisive, which starts with all data points in one cluster and recursively splits them into smaller clusters.
Fuzzy Clustering: Fuzzy clustering is a type of clustering algorithm that allows data points to belong to multiple clusters with different degrees of membership. It is useful when data points have ambiguous membership or when there are overlaps between clusters.
Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection, also known as outlier detection, is a machine learning technique that involves identifying data points that deviate significantly from the normal behavior or pattern in a dataset. Anomaly detection is used to identify unusual, rare, or abnormal data points that do not conform to the expected behavior of the majority of the data points. We can use statistical methods, clustering-based methods, or distance-based methods for anomaly detection.

Image from: DeepAI
For classification and clustering exercises, open the following Jupyter Notebook:
Loading last updated date...