Setting up your system with Python & Anaconda
Anaconda is an open source tool for organizing and setting up your Python environment. It handles dependencies, organizes Python libraries, and allows you to have multiple instances of Python set up on your machine without trouble.
Get started with Conda
Getting started with Conda from Navigator
Open navigator and go to “Environments”.

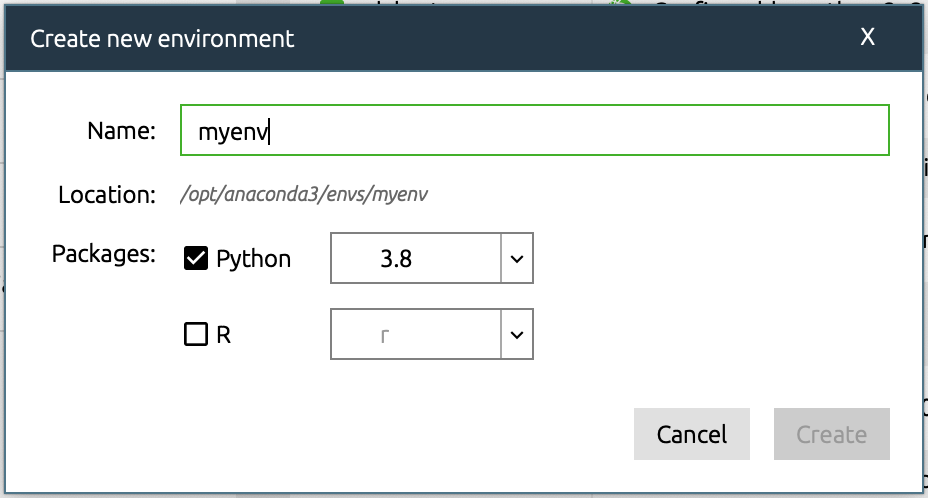
Create a new environment by selecting “create”.

Select the version of Python you want to work with. By default Anaconda selects the most recent version, in this case Python 3.8 which is fine for this workshop. Choose a short, descriptive name with no spaces.
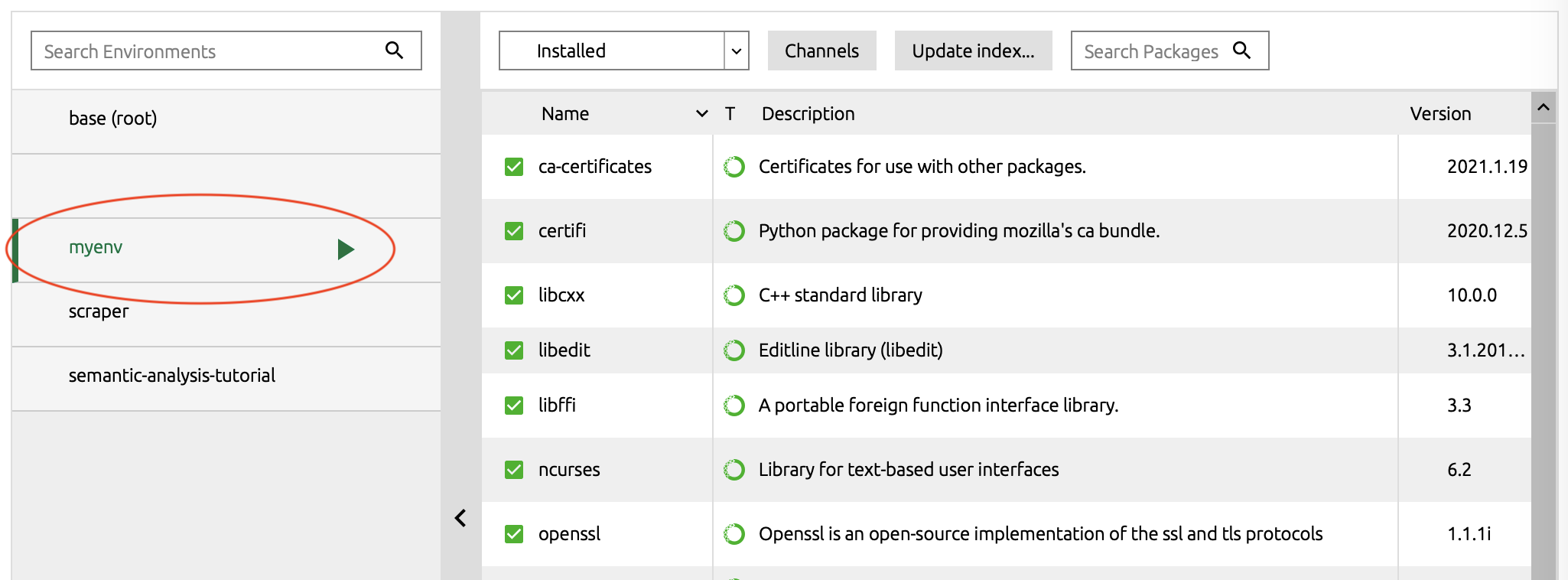
You should see your new environment in the left hand column. Clicking on the name of the environment activates the environment which is indicated by a green triangle or “play” button.
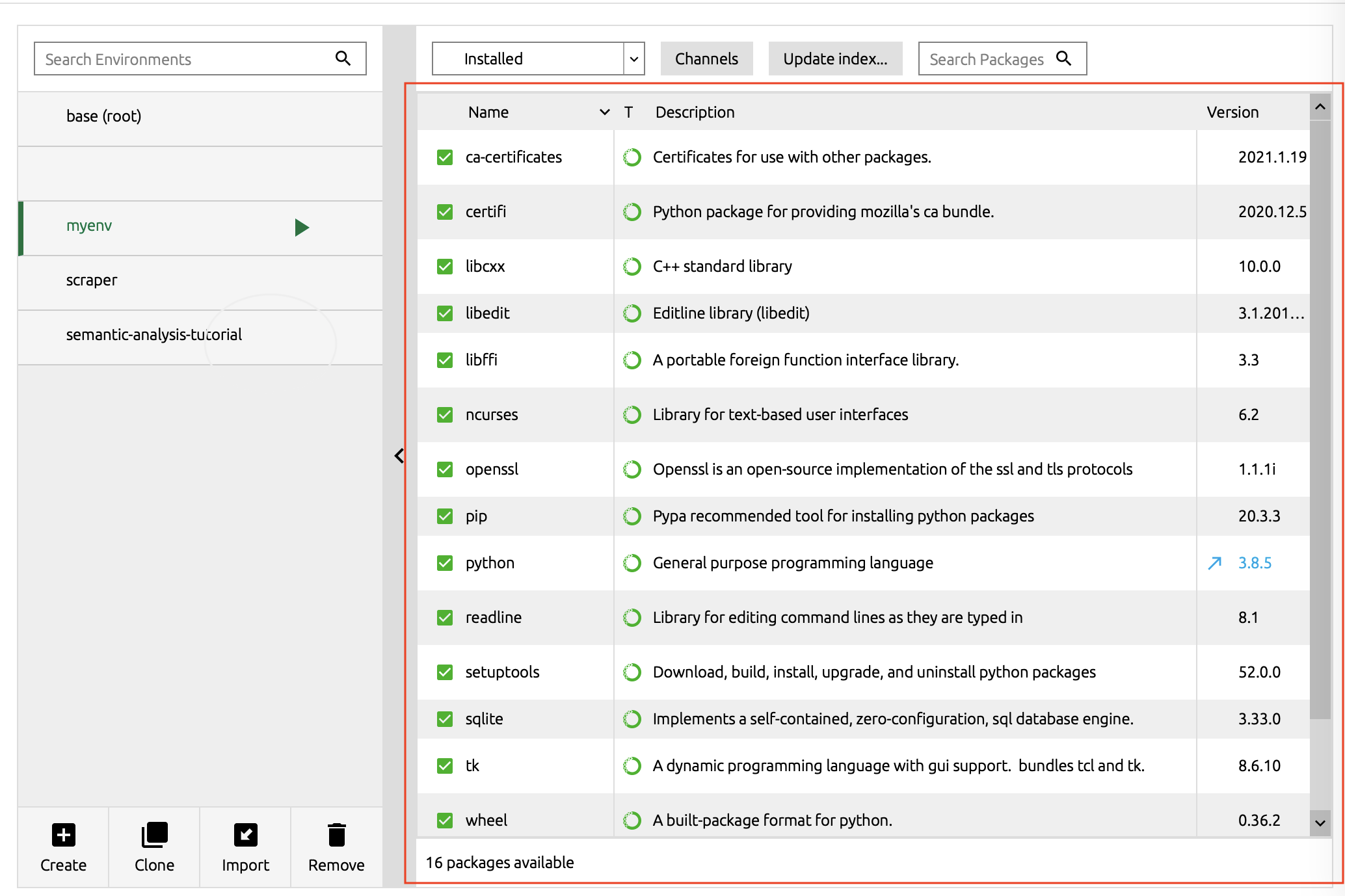
All Python libraries that are currently in the environment are listed on the right hand side.
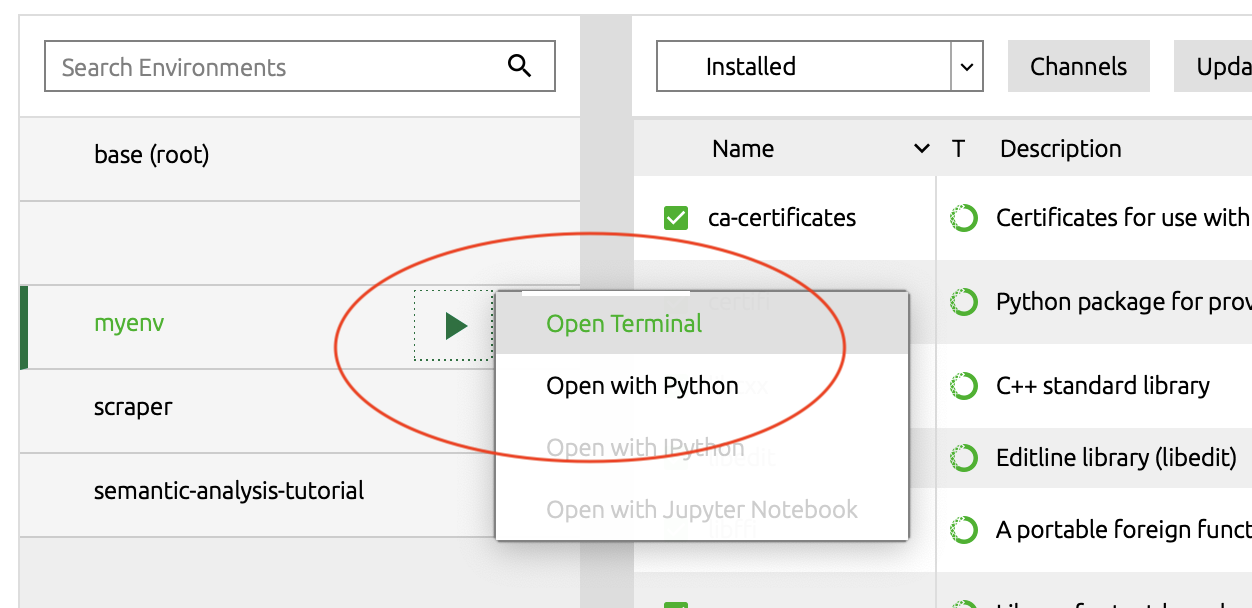
To start using your new environment, click on the green “play” button and select “open in terminal”.
Using Anaconda without Navigator
To get started with Python we need to create a new Anaconda environment using the “conda” command. This calls on Anaconda to make a new bucket with the correct environment variables for a given version of python.
The base command is as follows where “myenv” is the name of your new environment.
Input
conda create -n myenv
And if you want to specify a specific version of python you can add it after the base command.
Input
conda create -n myenv python=3.6
Once created you need to activate the environment to use it.
Let’s say you’ve made several environments and want to double check or delete what you’ve done.
Input
conda info --envs
Activate conda environment
Input
conda activate myenv
and check it is correctly set up.
Input
conda env --list
More on conda commands and environment management here: https://docs.conda.io/projects/conda/en/latest/user-guide/tasks/manage-environments.html#updating-an-environment {.note}
Installing Python libraries
Generally the easiest way to install Python libraries is using “pip” which is a command line tool. To begin with we need to install NLTK (Natural Language ToolKit) using pip.
Input
pip install nltk
Loading last updated date...