Table of contents
In this workshop, we only showed the basic features of Git. Git and GitHub have many more features. Here, we list a few of them:
GitHub and Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code has integrated source control management and support Git. You can also install other source control providers through VS Code Extension Marketplace.
The source control icon on the Activity Bar indicates an overview of the changes in the current repository. You can also open it using Ctrl + Shift + G shortcut. If you do not have a repository, you should create one first. The Introduction to Git and GitHub workshop covers the basics of Git and how to sync your local repository with GitHub.
In VS Code, you can stage and commit changes using the graphical user interface or by the terminal.
Graphical user interface for Git
Some terminal shells use some simple graphics to communicate a great deal of information about the current status of your git repository.
Zsh is highly customizable and Oh My Zsh is a community-driven framework that provides lots of plugins and themes to enhance your command line experience. For example, you can view the state of your Git repository right inside the terminal. You can install Oh My Zsh here.
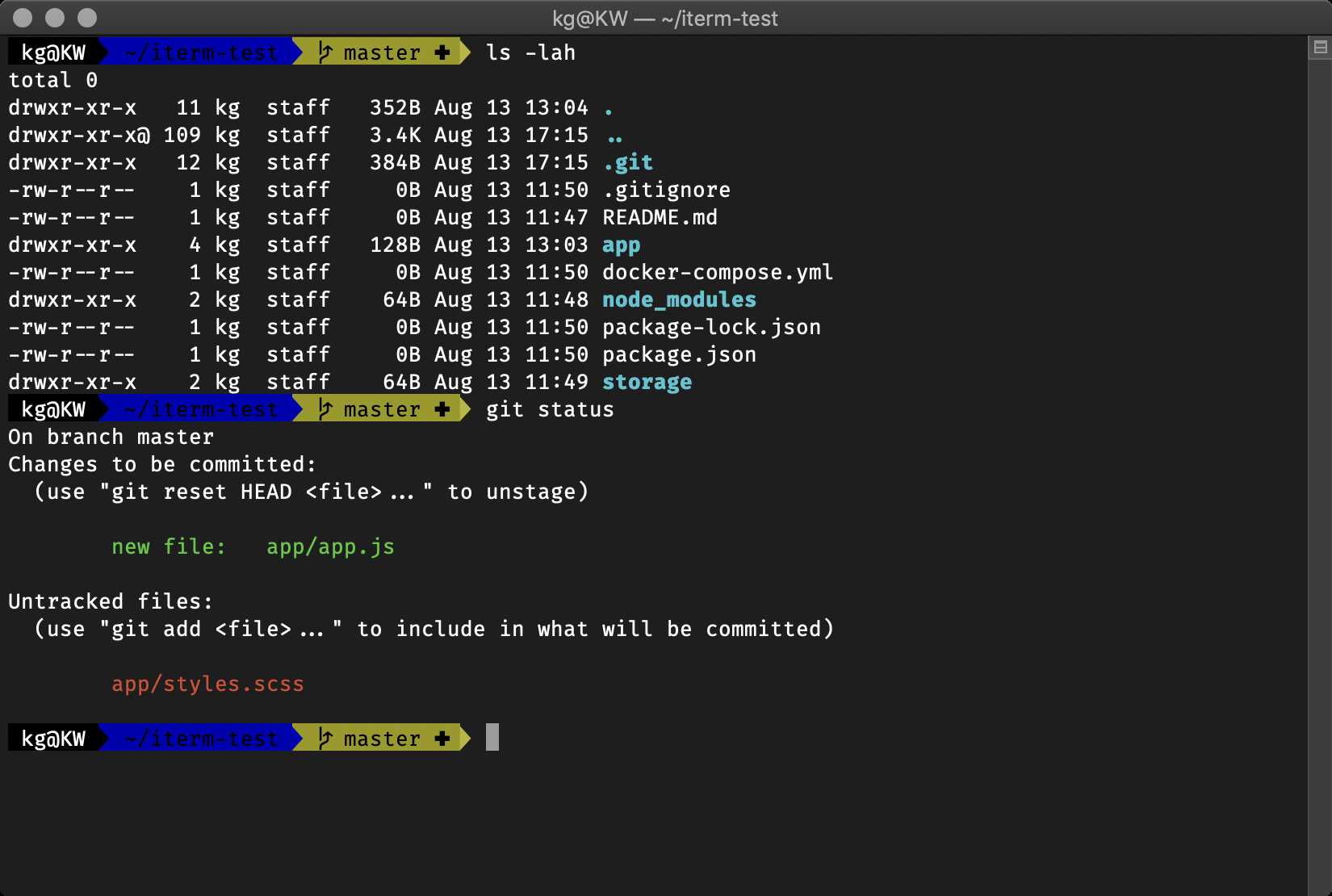
Zsh with agnoster theme
Example: Source Control with VS Code
To use source control tools in VS Code, you need to install Git on your machine. You can download the latest version on Git Website. When VS Code detects a Source Control Management Provider, it will show the git repository automatically and any changes will be displayed in the Activity Bar.
To track a project, you only need to click on the git symbol in the Activity Bar and initialize a repository. When you add a .gitignore file to your repository, VS Code automatically updates the visual indicator for files that you want to be tracked and filters out the files that you want to ignore.
If you click on any files in the Source Control view, VS Code will show a diff, which compares the new file with the old file in your repository and flags the changes. You can stage and commit changes one by one or all at once using the buttons available in the Source Control view.
You can push the local repository to GitHub using the Push or Push to… commands in the Source Control view. If you cloned the repository before, Push command syncs the local changes. If you want to build a new repository and push changes, use Push to… command.
You can create and checkout branches directly within VS Code by selecting Git: Create Branch and Git: Checkout to commands in the Command Palette. After running Git: Checkout to, you will see a dropdown list containing all of the branches and tags in the current repository. You can also create a new branch in the dropdown list.
If you have a Source Control Management Provider in the workspace, Git Status Bar will be added to the Status Bar that shows the current checked-out branch. You can Publish the current branch to a remote or Synchronize Changes which will pull remote changes down to your local repository and then push local commits to the upstream branch. To learn more about the capabilities of Git Extension in VS Code, check out the Source Control in VS Code webpage.
Loading last updated date...