Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Learning Objective 1: Understand what a GIS is, and the advantages to using QGIS.
GIS is an abbreviation for Geographic Information System. A nice description of GIS that provides a bit of relevancy comes from QGIS’s A Gentle Introduction to GIS:
Just as we use a word processor to write documents and deal with words on a computer, we can use a GIS application to deal with spatial information on a computer
With that in mind, there are 3 main forms of GISs:
-
Utilities and Services (tasks) - Scripts and programming libraries that manipulate spatial data in specific ways. For example, geocoding services geolocate a set of points based on address or coordinate attribute data. For example, MMQGIS is a QGIS plugin which contains a tool for geocoding.
-
Desktop (analyses) - Software that provides a suite of tools for processing and spatially analyzing data. In other words, GIS applications you interact with through a graphical user interface from a computer. Examples include the QGIS desktop app we will use today and Esri ArcGIS Pro. GRASS is another GIS.
-
Infrastructure (management) - Server and web resources that manage, curate, and distribute collections of spatial data. While Esri offers Server web services with ArcGIS Online, many open source GIS servers are out there.
There are a variety of GIS available, some proprietary and some free and open source. Free and open source means… It is for this reason that Research Commons workshops on GIS and Mapping use QGIS, a popular free and open-source GIS you can download directly to your computer.

QGIS is a popular desktop GIS software, and considered a free and open source software (FOSS) with a very active developer community. Take a moment to browse their website.
QGIS Advantages ⇡
- QGIS is free and open source, meaning you can download it directly from the web to your personal computer.
- QGIS runs on Windows, Mac, Linux, operating systems, meaning you don’t need a specific kind of device to use it. Some proprietary and costly software, such as ArcGIS, only run on Windows computers making it difficult to use without specialized equipment.
- QGIS has extensive online documentation, including a comprehensive official User Guide and Training Manual, as well as numerous YouTube and internet resources/tutorials created by users like you.
- QGIS has an intuitive interface which can be customized by the user.
- QGIS has an active development and user communities, meaning people are constantly posing and answering questions on platforms such as Reddit, StackExchange, and YouTube. This makes troubleshooting a whole lot easier. There is also an annual QGIS User Conference!
- QGIS has a robust plugin repository for extended functionality. This means the application you download to begin with doesn’t contain every single tool available, just the necessary and commonly used ones.
QGIS Disadvantages ⇣
- Most recent features can be buggy, which is why we recommend always downloading the latest Long Term Release, often small hyperlink below main download button.
- Plugins lack standardized documentation as they are largely user-community developed and contributed
- Troubleshooting often amounts to searching the web, though this is an important skill to have as a cartographer.
- Not ideal for more elaborate spatial analysis or network analysis workflows.
QGIS Resources
QGIS itself has extensive online documentation, including a robust User Guide and Training Manual.
QGIS also has a vibrant user community, with answers to nearly any question you might have only a web search away. Many helpful tutorial demonstrations can be found on Youtube. For instance, CWU Geography offers especially clear and helpful content, but there are many, many others.
Once you’ve reviewed this GIS 101 workshop, we invite you to attend any of UBC Research Commons’s mapping with QGIS workshops (colored teal in the Events Calender here):
- Intro to Map Production with QGIS
- Reference Mapping with QGIS
- Thematic Mapping with QGIS
- Tools and Workflows in QGIS.
- Plugins with QGIS
The best way to learn QGIS is through the experience that comes with hands-on practice. QGIS has with a medium learning curve, especially if you’ve never used a GIS before. However, don’t let this dissuade you! The abundance of QGIS-official and unofficial documentation means you can tailer your learning experience to your interests and the specific needs of your project.
Downloading & Installing QGIS
QGIS can be downloaded from qgis.org’s Downloads page. In most cases, you’ll want to download and install the Long term release instead of the latest release. This will give you most of the functionality you’ll need without encountering the software bugs of newly released versions.
To Do
Install QGIS for your operating system. From qgis.org’s Downloads page, select your computer’s operating system from the drop-down menu.
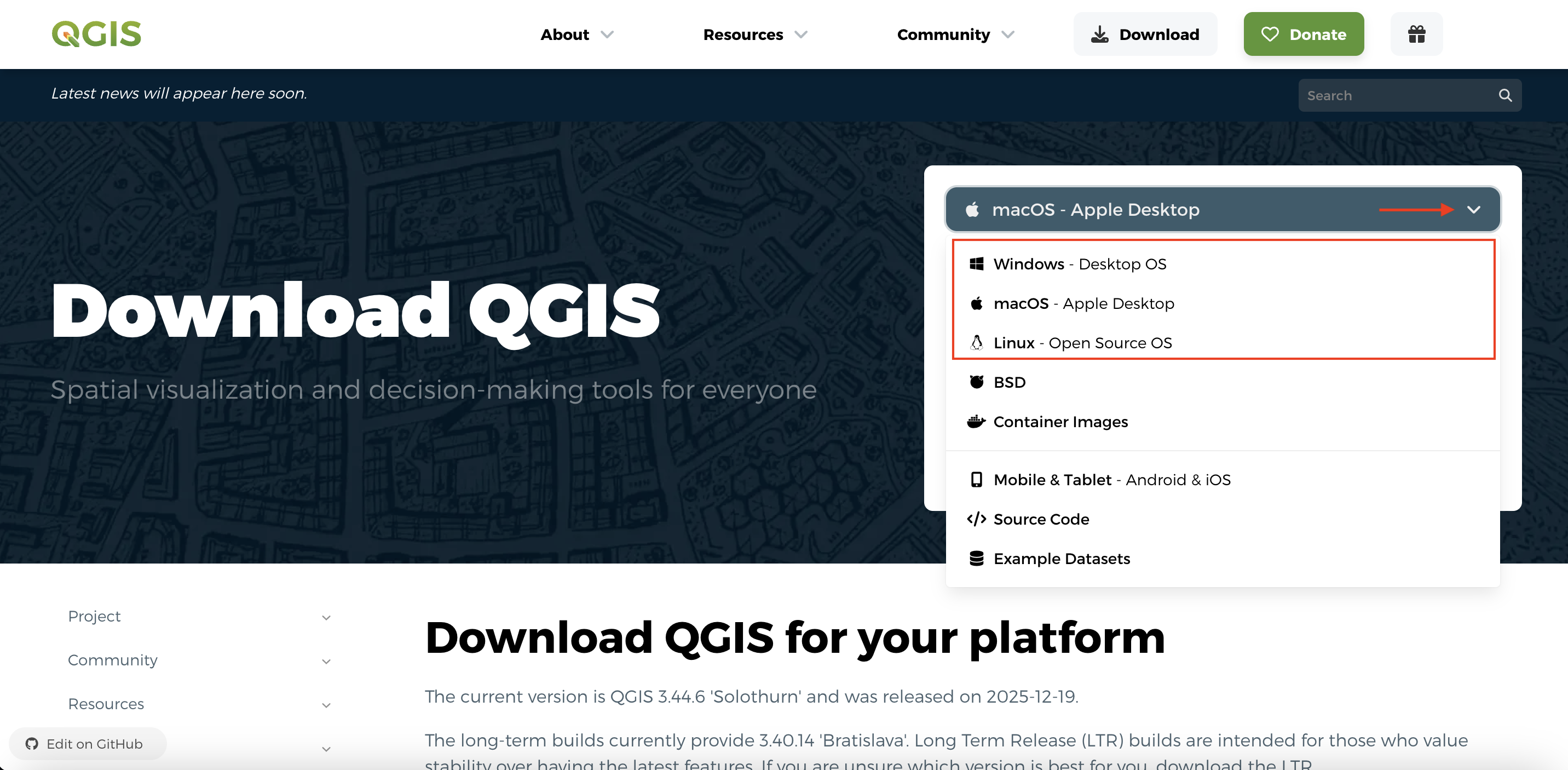
For Mac, choose the “Regular Version for macOS”

For Windows, scroll down and choose the Long Term Release
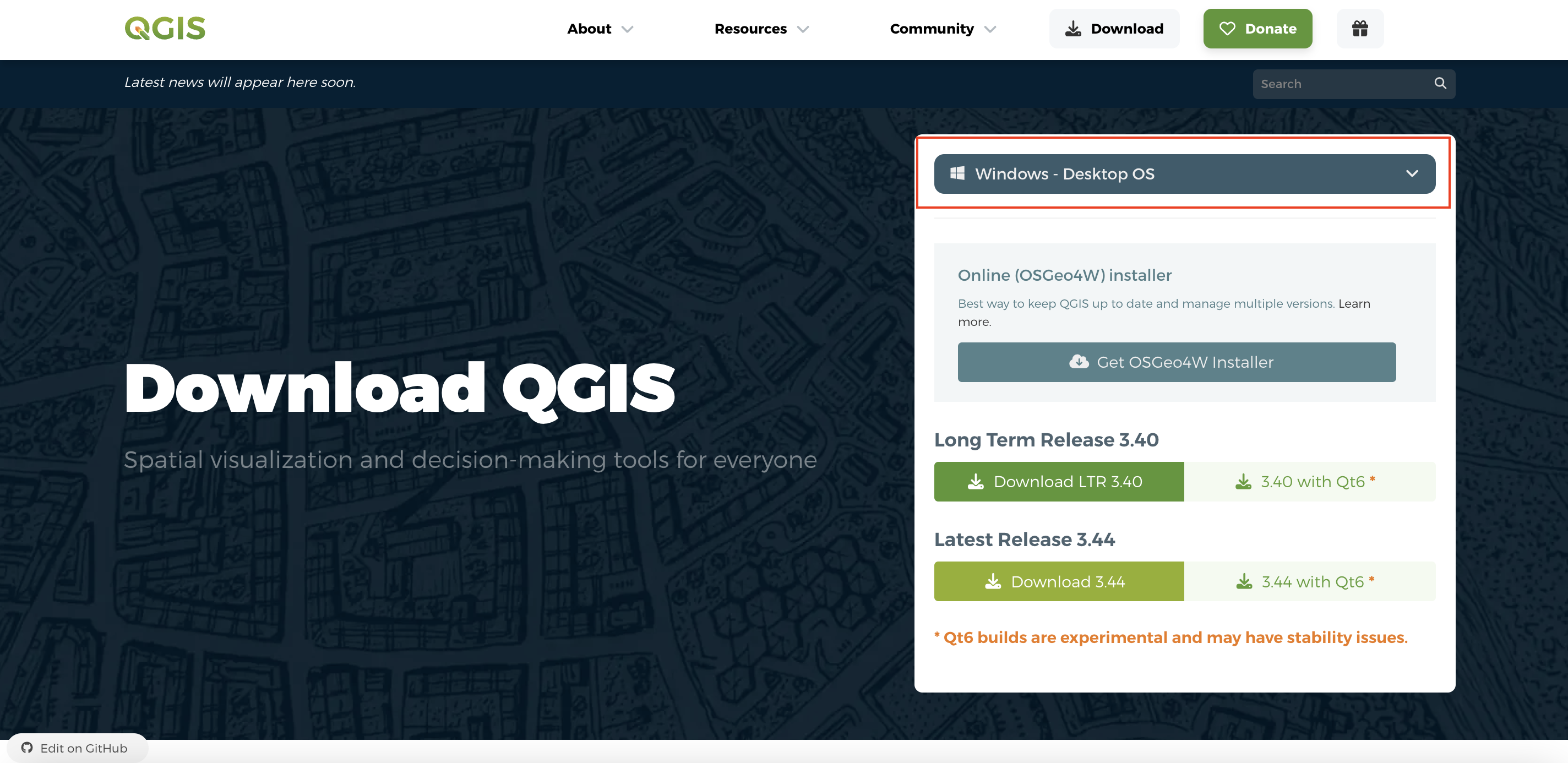
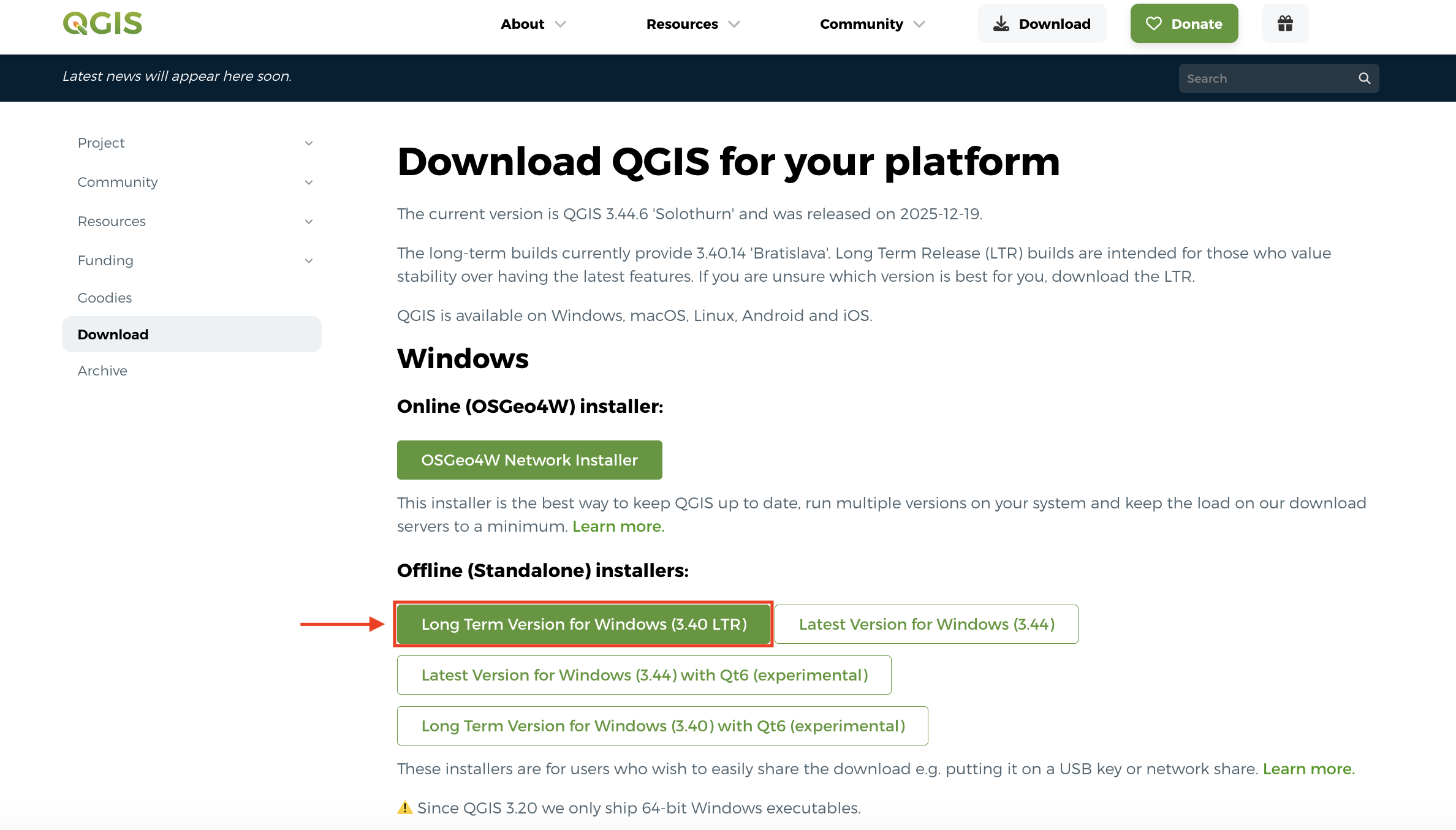
Later on in this workshop, you will be given a tour of the interface, as well as guided through adding data to a project and saving your project. For now, just make sure you have properly downloaded QGIS and are able to launch it. See below for troubleshooting tips if you’re working on a Mac computer.
Troubleshooting
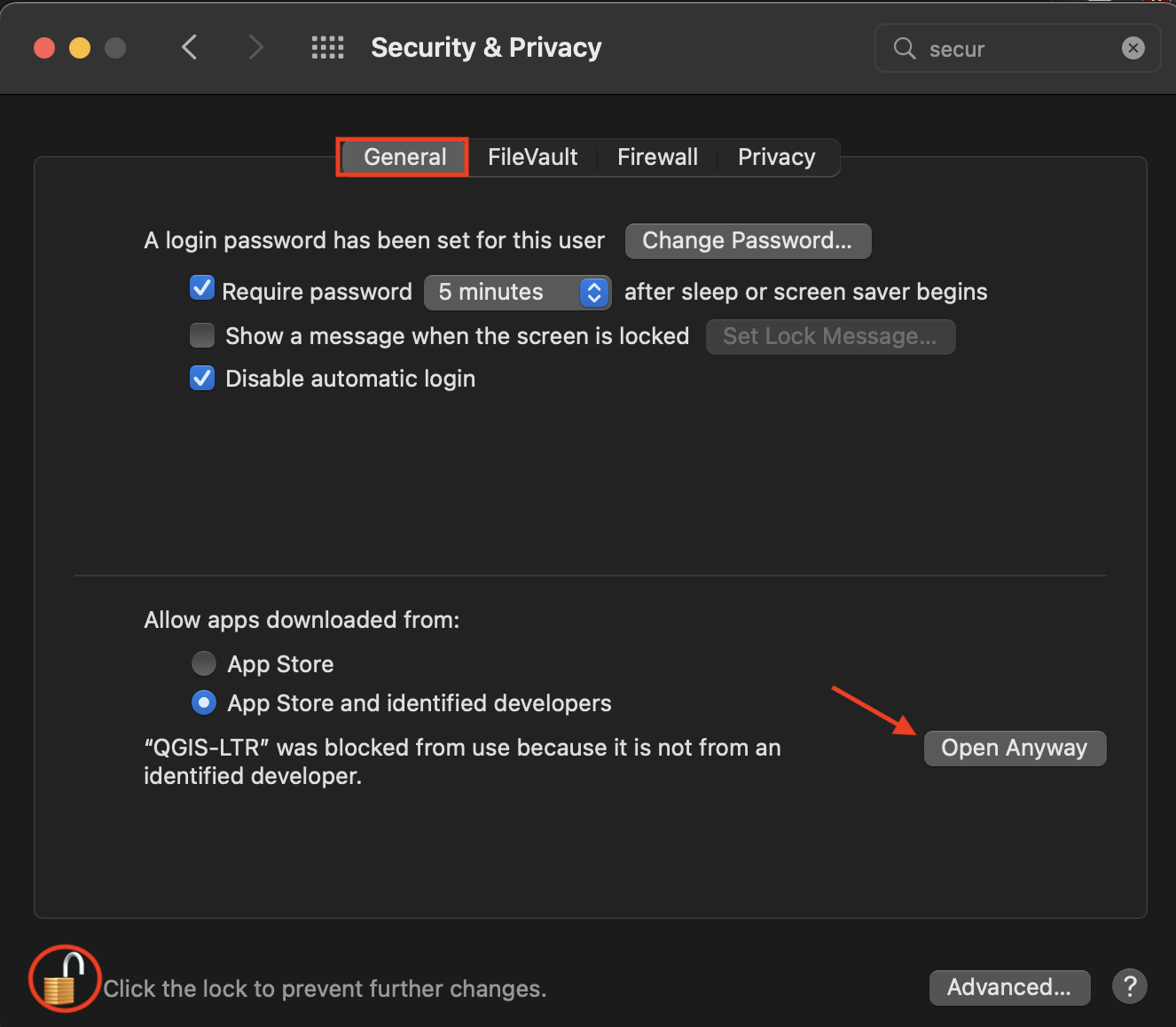
If you’re working on a MacOS and get the message: “QGIS-LTR can’t be opened because Apple cannot check it for malicious software” when you try to open the application, go to System Preferences –> Security & Privacy –> General and unlock your settings. At the bottom of the dialogue box you will see an option to Open Anyway. Click that, then re-lock your settings and try again to open the QGIS-LTR application.
Loading last updated date...