Geocoding Address Data
Geocoding is a process by which addresses are given coordinate locations, thus allowing them to be manipulated in a GIS. In other words, geocoding transforms tabular data into spatial data. Reverse Geocoding is when you begin with a set of geolocated points (coordinates) and use a tool to get the street addresses of each point. This page will guide you through geocoding using the MMQGIS plugin.
1 From the workshop data folder, add libraries.csv to your QGIS project. This is a list of libraries in Vancouver, also downloaded from Vancouver’s Open Data Portal. Because it is tabular data (in the form of a .csv, or comma separated value table) and not a spatial layer, nothing will show up on your map. Take a look at the attributes of this table. You’ll see there are street address as well as city and country attributes. We’ll use these to geocode this dataset.
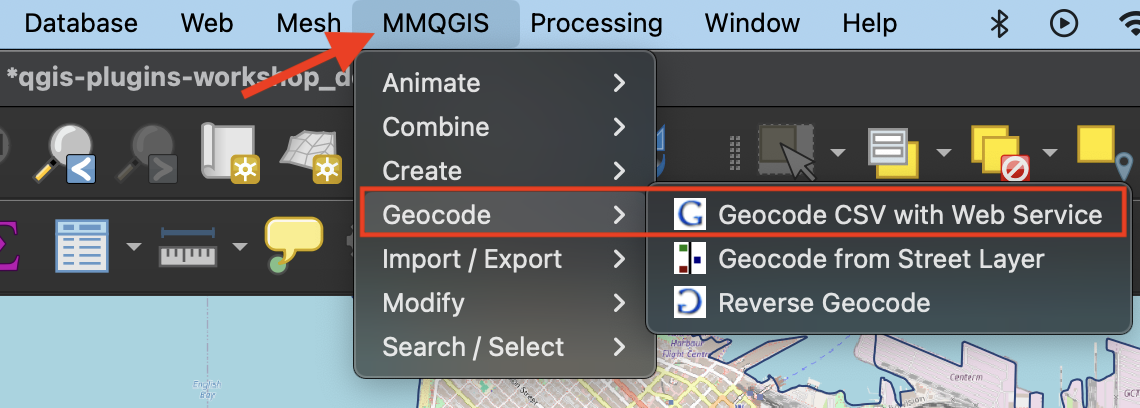
2 Install MMQGIS plugin from the Plugins Manager. You’ll see it adds an entire menu to the top of your screen. Take a look at different options. Choose Geocode CSV with Web Service.
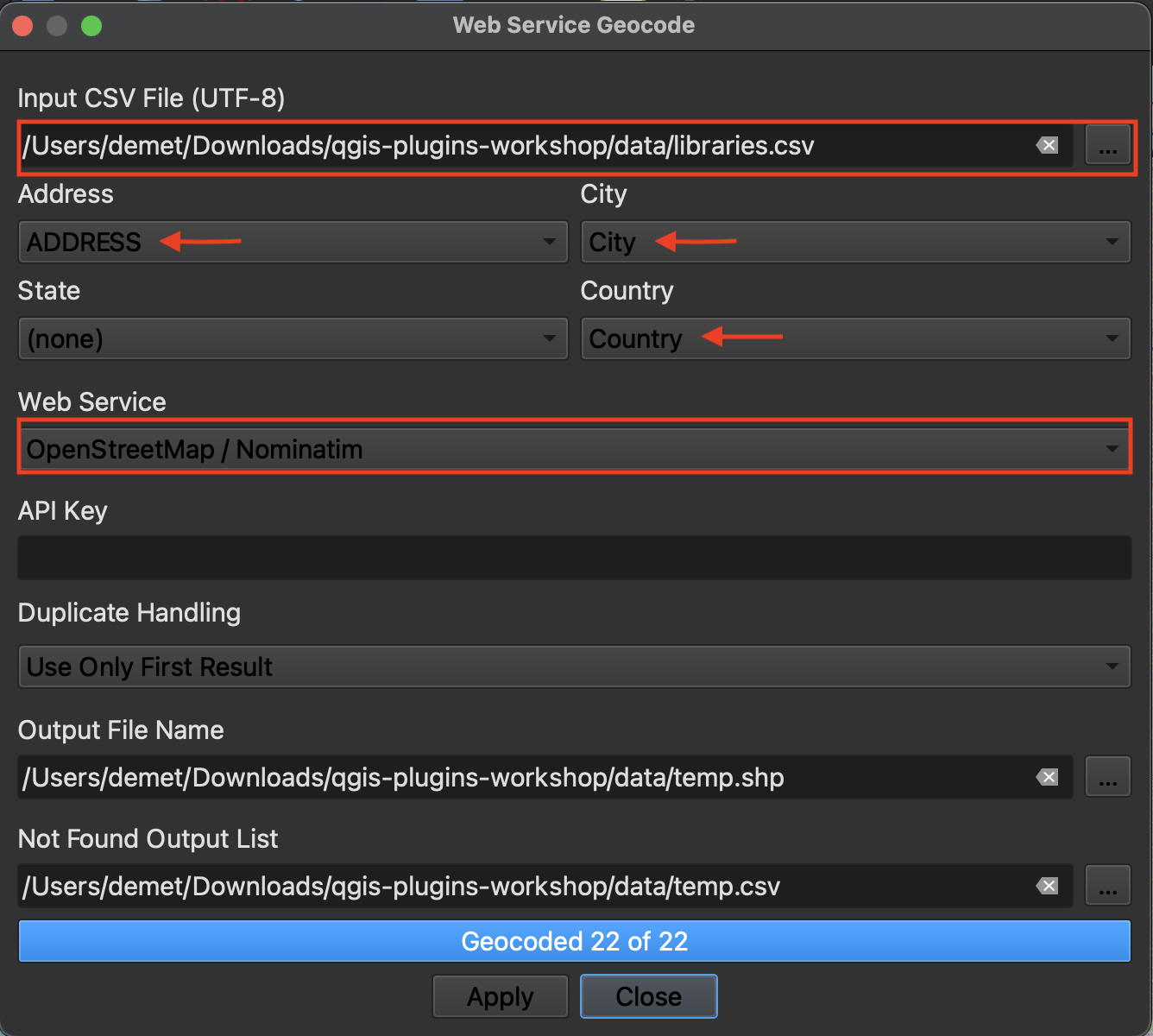
3 In the geocoding window that opens, chose the libraries.csv file as your input and leave the outputs as temporary files. The address, city, and country properties will likely auto-populate since the column names directly reference the input fields. Sometimes you do have to manually match the properties.
Change the web service to Open Street Map / Nominatim. Hit apply. There are 21 rows in the library dataset so 21 points should be geocoded. The output csv that indicates what wasn’t matched should be empty.
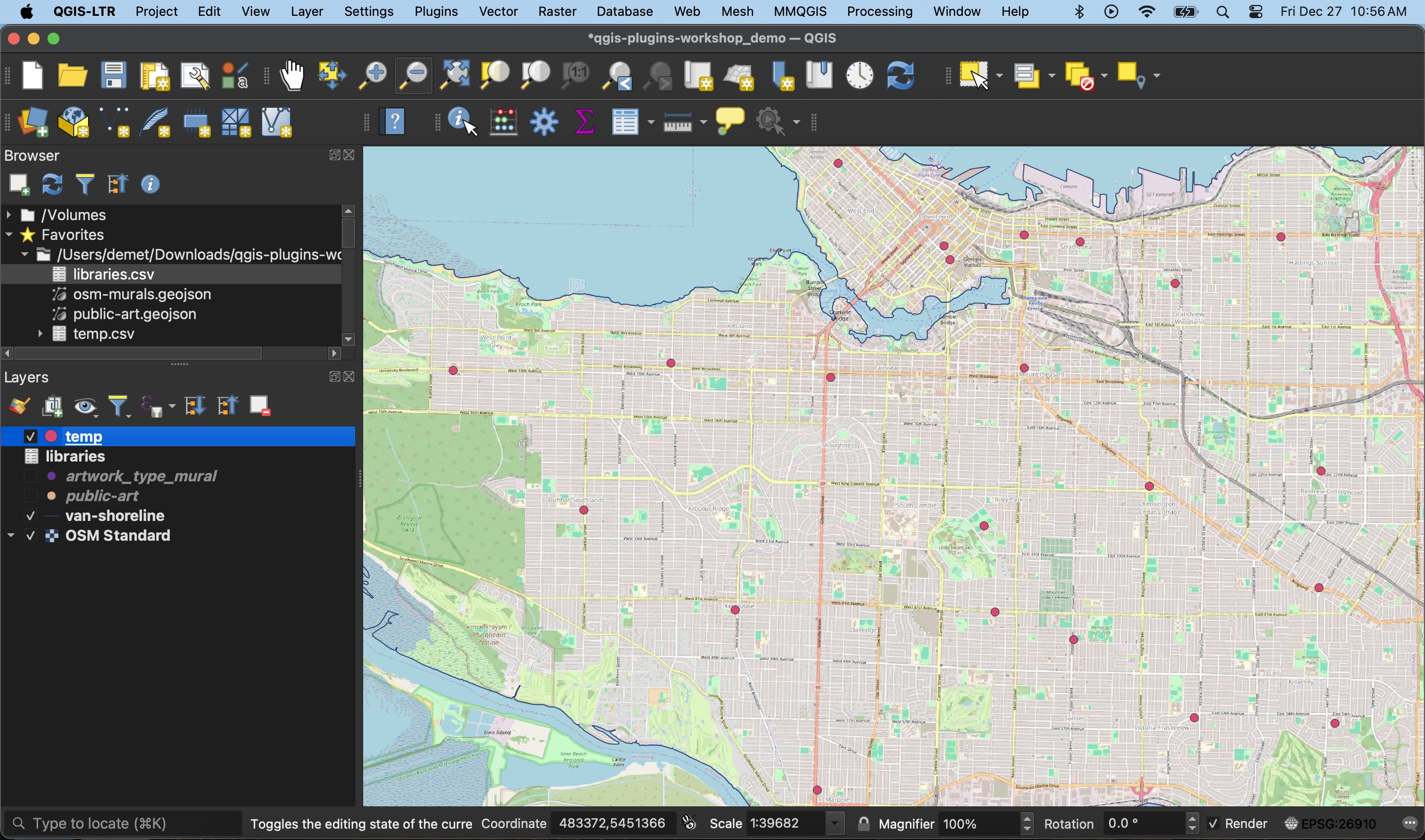
4 If you want to save your geocoded output as a spatial data layer, simply save the temporary file as a permanent layer. To do this, right-click the layer and Export it, giving it a name and appropriate storage location.
Resources
- See another GeoCoding, another plugin specific to finding addresses or reverse geocoding
-
See another resource on Geocoding plugins
- You don’t need to geocode in a GIS! If you aren’t using a GIS for any other portion of your project, consider using an online geocoder like BC Address Geocoder or geocodio, or explore more free and paid options here
Loading last updated date...